End of Financial Year Planning
With 30 June looming around the corner, it’s important to take time out to get your financial affairs in order. We’ve compiled some of the items that should be high priority on everyone’s list.
Concessional contributions (pre-tax)
The annual concessional cap is currently $25,000. Concessional contributions include employer contributions, salary sacrificed and personal contributions claimed as a personal deduction. The concessional contribution tax rate is 15%.
High income earners, individuals earning $250,000 or more, will pay an additional 15%, on top of the standard 15% contributions tax.
Concessional contributions for this financial year and taxable income should be reviewed, to determine if a top-up is beneficial. The potential for a carry-forward concessional contribution strategy is also now a consideration.
Carry-forward concessional contributions
Since 1 July 2018, any unused amounts in an individual’s concessional contributions cap can be carried forward on a rolling five year period if the individual has a total superannuation balance under $500,000 at the end of the previous 30 June.
For example, if David made concessional contributions of $10,000 during the 2018-2019 and 2019-2020 financial years, and his total superannuation balance on 30 June 2020 was $200,000, David could make a $55,000 concessional contribution during the 2020-2021 financial year (unused cap from 2018-19 and 2019-2020 FY cap plus 2020-21 FY cap).
The concessional contributions cap will be indexed to $27,500 from 1 July 2021.
Non-concessional contributions (post-tax)
The annual limit for non-concessional contributions is $100,000, if an individual’s total superannuation balance is below $1.6 mil, as at 30 June 2020.
The bring-forward rule, which allows the contribution of three years’ worth of non-concessional contributions ($300,000) in one year, is available to eligible members provided they have not triggered the bring-forward rule in the past two financial years and their total superannuation balance was less than $1.4 mil, as at 30 June 2020.
Individuals with a member balance between $1.4 mil and $1.5 mil may be able to utilise part of the bring-forward rule.
For example; James aged 58, is starting to plan for retirement. He has $500,000 in cash in his own name and a total superannuation balance of $800,000. James decides to utilise the bring-forward rule to contribute the $300,000 to superannuation as a non-concessional contribution to invest in the share market. No further non-concessional contributions can be made in the next two financial years.
The non-concessional cap will be indexed to $110,000 and the total superannuation balance restrictions will increase from $1.6m to $1.7m from 1 July 2021.
Superannuation contribution work test
The work test is still a requirement for anyone over age 67 wishing to contribute to superannuation. To satisfy the work test, an individual must be gainfully employed for at least 40 hours during a consecutive 30-day period during the financial year in which the contribution is made, prior to the contribution being made.
Work test exemption (WTE)
Since 1 July 2019, individuals aged 67 – 74 may be able to make additional voluntary contributions for the 12 months from the end of the financial year in which they last met the work test, if they meet the following three criteria:
1. Their total superannuation balance was under $300,000 on 30 June the previous financial year
2. They met the work test the previous financial year
3. No WTE contributions have been received in a prior financial year
For example, Steven retired on 30 June 2020 aged 68 with a total superannuation balance of $150,000. On 12 August 2020 he sold his investment property to realise the capital gains in the year he was not working and had a lower taxable income, then made both a concessional and non-concessional contribution with the proceeds before 30 June 2021.
Superannuation pension payments
Pension payments and minimum and maximum limits should be reviewed. It is vital that accurate figures are obtained for each member as penalties may be imposed for over or under payment.
Superannuation members should keep in mind that the Government has temporarily halved the usual minimum pensions required for the 2020-2021 financial year to minimise the likelihood that members would have to sell assets in a depressed market if they did not have enough cash available.
The standard and revised minimums are as follows:
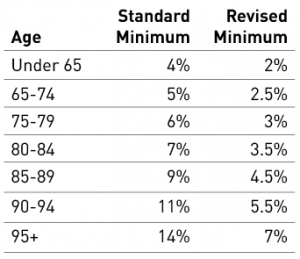
The maximum transition to retirement pension remains at 10%
For example, Jane, aged 68, has an SMSF valued at $480,000 on 1 July 2020. Her usual minimum is $24,000 (5%) which she generally elects to draw as a single payment in June. However, this year with her balance reduced and minimal cash in the fund, she is able to take advantage of the temporarily reduced minimum of $12,000 (2.5%).
The Government announced the minimum pension reduction will be extended for the 2021/2022 financial year.
Superannuation contribution splitting
The $1.6mil pension transfer cap on funds in the tax-free pension phase has made it more important than ever for couples to maintain even account balances. Superannuation splitting allows a member with a higher account balance to transfer up to 85% of their concessional contributions to their spouse (the 15% contributions tax is deducted before splitting).
The receiving spouse must be less than their preservation age or aged between their preservation age and 65 and not retired. The splitting application should be completed in the financial year immediately after the financial year in which the contribution was made or in the same financial year if the account is being closed.
The pension transfer cap will be indexed to $1.7mil from 1 July 2021.
Consider whether you have met a condition of release
Anyone who has reached age 60 should be aware of the potential conditions of release that would allow them access to their superannuation and commence a tax-free Account Based Pension. As part of an end of financial year review, determining if a condition of release is met could provide significant benefits.
The most common conditions of release include retiring post preservation age and reaching age 65 regardless of work status. However, a little known condition is ceasing an employment arrangement on or after the age of 60. This condition is even met if you have two employment arrangements and only cease one while the other continues.
Government co-contribution
Anyone with an adjusted taxable income of less than $54,837 can take advantage of the government co-contribution, however the maximum benefit of $500 begins to taper down when their taxable income exceeds $39,837.
The government co-contribution is not available to individuals who exceed the non-concessional contribution cap or the total superannuation balance cap of $1.6 mil.
Spouse contribution
If an individual has an assessable income of less than $40,000 then their spouse is able to make a non-concessional contribution on their behalf and claim a tax-offset. The maximum offset is $540, where your spouses’ assessable income is $37,000 or less. The offset reduces as the receiving spouse’s assessable income increases above $37,000 and is phased out at $40,000.
Get in touch
If you would like to discuss any of these strategies further, please contact your Bell Potter adviser.
